Digital Identity
About ShareRing
ShareRing is a Digital Identity Service Provider (IDSP) focused on developing Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) solutions and institutional grade verification technology to enable friction-less interactions between businesses and their customers to give users control over their digital identity and simplify the process for businesses verifying customer's identities.
What is Digital Identity?
A digital identity is comprised of the data that allows you to uniquely identity yourself online. Your digital identity includes information about you, for instance:
- Name
- Date of Birth
- usernames
- Passwords
- Identification details (for instance, your driver's license number)
- Credit Card numbers
You use aspects of your digital identity every time you access an online service or make an online purchase.
Your digital identity also includes information generated by your online activities. For instance:
- Search history
- Social media posts
- Browsing habits
- Health data from your wearable devices
The amount of data that is generated everyday is already staggering and it's increasing all the time with new services, devices, and ways of collecting data.
The Data Never Sleeps 10.0 report shows that in 2022 per minute we collectively made 5.9 million search queries on Google, shared 1.7 million pieces of content on Facebook, and spent $443,000 on Amazon.
That's per minute, and almost every interaction online forms part of somebody's digital identity.
At ShareRing, we believe individuals should have full control and ownership of their digital identity, and that the next phase of evolution in digital identity should put users in control of their data.
The Evolution of Digital Identity
Digital identity has gone through three distinct phases:
- Centralized Identity
- Federated Identity
- Self-Sovereign Identity
Centralized Identity
Websites that store username and password combinations for their users on the same servers that host the website are an example of centralized identity. When users log in, their entered username and password are validated against the record on the server's database, the user is logged in and can access the website if there is a match.
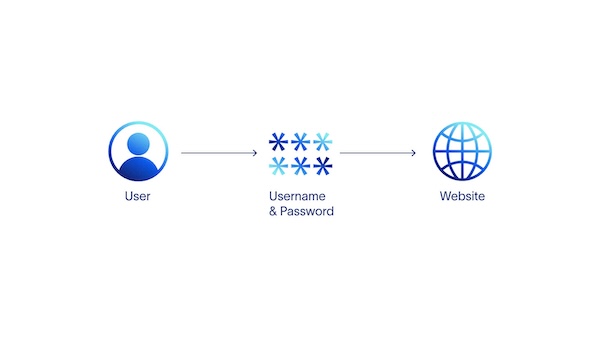
In the centralized identity model, every website with a login that a user visits stores a username and password combination for that user. A user's digital identity in a centralized identity framework is fragmented. Each server that sorts a user's username and password, represents a vulnerability that can be hacked and put users' identities at risk.
Federated Identity
Federated identity aims to solve the challenges of centralized identity by consolidating digital identity with a central provider. The rise of social media giants and digital platforms like Facebook, Microsoft, and Google allow digital identity verification through these platforms instead of using a separate username and password combination for every website or service.
In the diagram below, users verify their identity through an account held by a third-party identity provider. These providers have a trust agreement with external websites, and the user can log in to these websites using existing credentials.
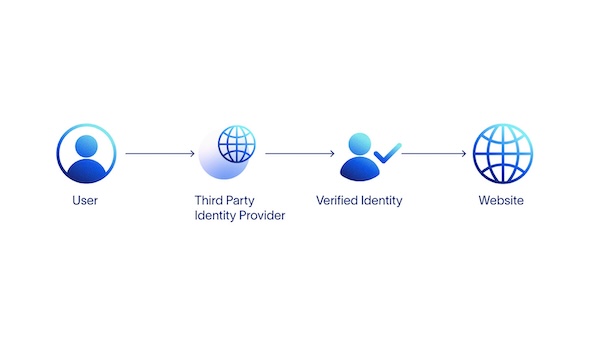
Federated identity has dramatically simplified the login process for many users. The benefits are convenience and added security because a single login service validates identity on multiple sites. However, using a federated login service, means the service now has access to a wide range of information about the user. A user could be banking, purchasing goods, browsing websites, or reading articles on social media. These are isolated data points individually, but together these form part of a user's digital persona.
Federated identity raises an ethical concern because companies can use this information to display targeted advertisements or news articles to influence a user's behavior. Even if the companies that provide the federated login service don't use this information, it exists on their servers and is a vary attractive haul to hackers.
Self-Sovereign Identity
Self-sovereign identity uses the principles of decentralization to give individuals control over their digital identity.
Self-Sovereign identity addresses the major concerns of centralized and federated identity and does NOT:
- Require individual usernames and passwords for every service you use.
- Entrust your digital identity to a single federated identity provider.
With self-sovereign identity, users verify and manage their digital identity from their personal devices in a digital wallet, and when they need to prove their identity they action the request by scanning a QR code and then approve the request. If the user decides not to approve the request, they simply reject the request.
With self-sovereign identity, the process is:
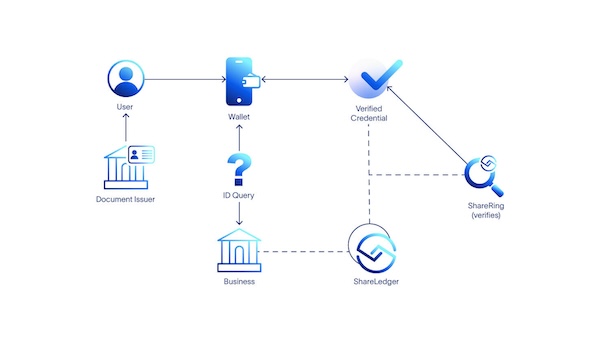
- A document issuer (for instance the passport office) issues an identification document to an individual.
- The individual uploads the document to the wallet on their personal device inside the ShareRing Me app.
- ShareRing performs a series of checks on the document to make sure it's genuine.
- The document becomes a verified document and ShareRing adds an asynchronous hash as a cryptographic proof to the ShareLedger blockchain.
- When a business needs to check a customer's ID, the customer uses the ShareRing Me app to scan a QR code from the business and approves the request for information.
- The response to the request is returned to the business along with the cryptographic hash from the ShareLedger blockchain to prove the information in the user's wallet hasn't changed since ShareRing verified it.
The ShareRing Solution
Users can download and use the ShareRing Me app to manage their digital identity, or for users looking for a web3 experience in addition to manage their digital identity we also have the ShareRing Pro app.
Businesses can create queries with ShareRing Link to generate QR codes their customers can scan to share verified credentials from the vault in either their ShareRing Me or ShareRing Pro apps.